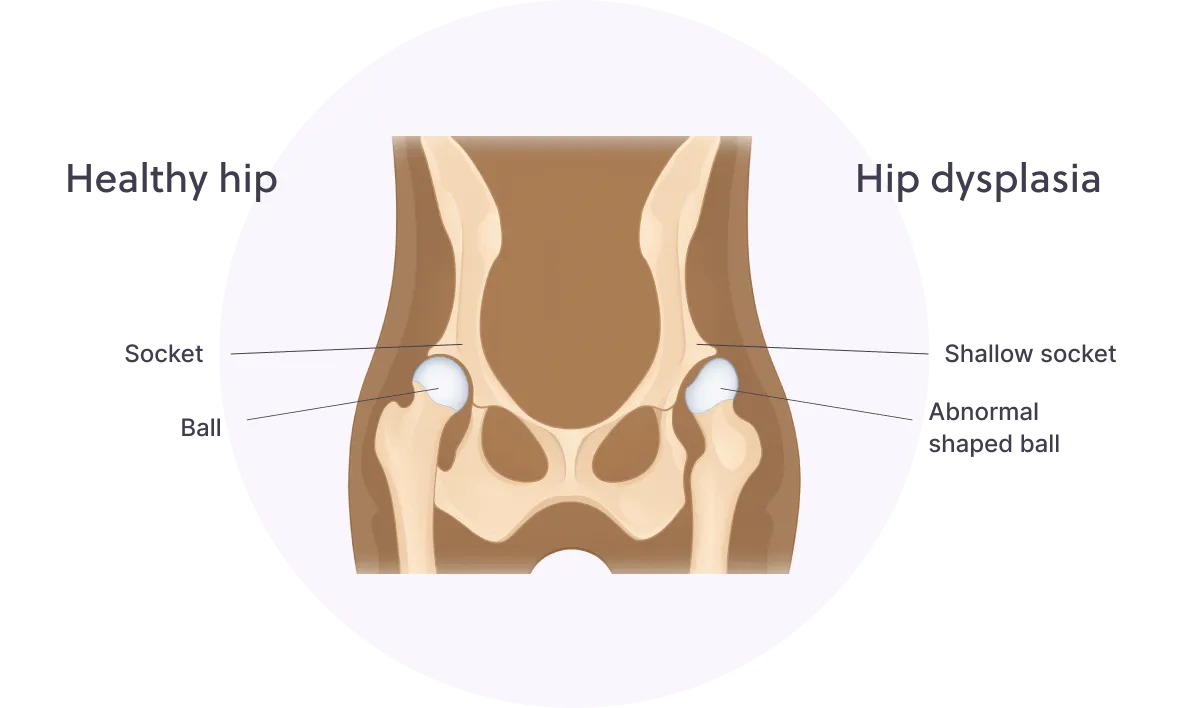
Pet Insurance
About Us
Members Benefits
Vets
Pet Hub
Insurance Hub
Tail Talk Blog
Contact Us
Pet Insurance
Pet insurance Info
Members Benefits
Become a Partner
How We work with Vets
Work with your Clinic
Vet News
DOG
CAT
Pet Insurance Hub
- Petsy Pet Insurance Explained
- Planning ahead
- Specified Conditions
- Understanding BOAS and Your Pet Insurance
- What's Covered with Petsy?
- Understanding Pre-existing conditions
- What is a pre-approval?
- The Ultimate Guide to Pet Insurance
- Understanding Pet Insurance
- How it Works
- Pet Insurance Glossary
- Pet Insurance FAQs
- Switching pet insurance providers
Insurance
Tail Talk Hub
- 50 amazingly fun things to do with your dog
- Becoming a pup-parent: The 6 essential development deadlines in a puppy’s life
- Everything you need to know if you’re thinking about getting pet insurance for your cat
- What to do if your dog gets stung by a bee
- Allergies in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms & How to Help Them
- Testing puppy form submit